Sustainability of products has a value for some clients who like to buy sustainable products or enter "functional business" contracts. Companies selling products must convince the buyers that products are made in sustainable ways -- from use of raw materials to finishing touches and recycling or disposing of the products. Thus sustainability management must follow a product life cycle.
In a "green" economy, sustainability is the capital or value in the market. Products that are not sustainable are at risk of being less attractive to clients and other stakeholders and companies in the business ecosystem and in the supply chain.
However, for products that meet demands of sustainability, there are many opportunities that must be considered in management control systems and cost and management accountants (CMAs) have a major role in this regard.
The idea behind sustainable business is that consumption of raw material must decrease in an environment-friendly way. New business models need to be set in order to achieve a higher level of sustainability. Recycling and disposal are key elements and they must be incorporated into the management control systems.
The choice of raw material is important. What values can companies achieve if they use either recycled material or new material? Whether a supplier is a sustainable supplier is another question that affects companies' material decisions. When an agreement is made to deliver material, the terms of transport are agreed. Sustainable companies need to consider not only the price of transport but also whether transport is environmentally friendly or not.
In construction and production of products, companies must include sustainable technology in the product and in fabrication processes involved. Products must also include recycling friendly solutions.
In markets, products must meet competition not only in terms of price but also competition that includes sustainability factors of products. The declarations or information of content and functions of products are sustainable reports made for buyers. This fact is important because it creates values in competition processes.
When products are used, selling or producing companies remain responsible. Several risks are involved in using products and they can damage values of the product brand and sellers.
When product life cycles end, information about recycling or disposal must be available to owners of products. Recycling firms need to have information about products in order to detoxify and recycle products. Which company will pay for detoxication and keep toxic material is a very important issue. The value of toxic material depends on technology in order to bring products back into a safe new life cycle. Disposals must be kept in secure deposits until new technology is found for recycling of the disposals.
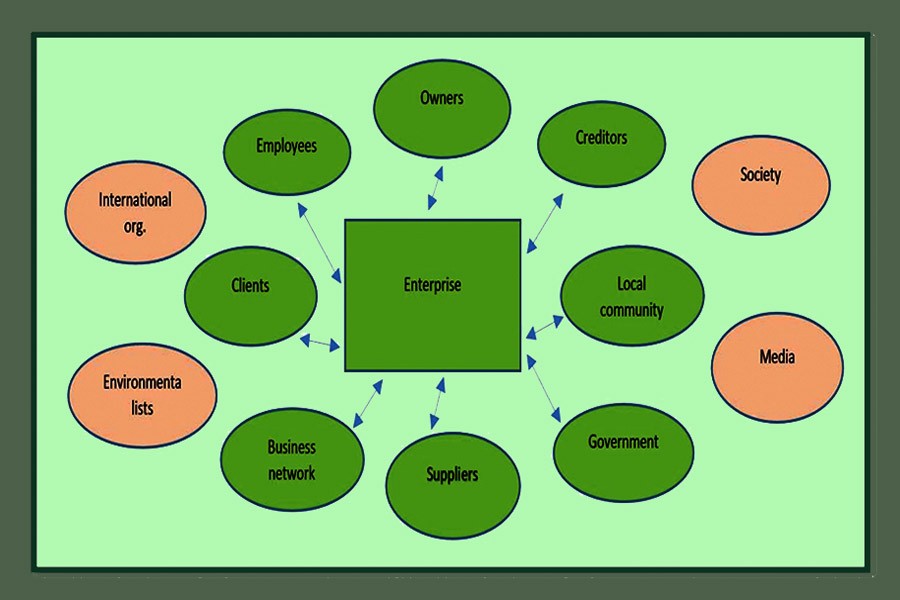
Value has different meanings for different stakeholders. Stakeholders who a) create value by bringing in resources and capabilities, which are firm specific, causally ambiguous and socially complex, and b) appropriate some of the value created in their relationship with the firm.
This broader stakeholder-based view of value creation activity offers a theoretical foundation to a stakeholder approach to economic valuation in which some stakeholders do obtain positive net present value. In a word, total value created by enterprises must also include value captured by stakeholders.
One ecosystem is the businesses network, another one is the environmental ecosystem, a third one is the technological ecosystem, and finally the human and social ecosystem is another. An enterprise cannot create long-term business value without synchronisation among other levels of ecosystems.
The financial sector provides various forms of capital for enterprises' financial needs. In return, financial firms receive interest and in some cases a portion of the value in the investment.
However, a tendency over the last decades is financial firms' growing interest in sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR), not only in the financial firms itself, but also in their product portfolio.
Encouraging environmentally responsible investments and prudent lending is one of the responsibilities of the banking sector. Further, those industries that have already become green and those that are making serious attempts to become green are accorded priority in lending by banks. This method of finance is called "Green Banking", an effort by banks to encourage industries to be green and in the process restore the natural environment.
And the central bank has already implemented the green banking model for each bank and financial institution since 2011. For the banking sector, green finance is defined as financial products and services, under the consideration of environmental factors throughout the lending decision making, ex-post monitoring and risk management processes, provided to promote environmentally responsible investments and stimulate low-carbon technologies, projects, industries and businesses.
Being a responsible corporate citizen and with a view to developing green banking practices in the country, the Bangladesh Bank issued on February 27, 2011 a circular (BRPD Circular No.2) on policy guideline for green banking towards banks stating "to adopt a comprehensive Green Banking Policy in a formal and structured manner in line with the global norms so as to protect environment degradation and ensure sustainable banking practices".
In line with the instructions of the Bangladesh Bank, all banks have taken initiatives to formulate its Green Banking Policy with an aim to inculcate practices towards optimum usage of natural resources and make every effort for environmentally friendly activities.
Green banking refers to the attempt of the banking sector to consider social, ecological and environmental factors with an aim to protect the environment and conserve natural resources. The banking sector plays a major role in financing investment for commercial projects, which is one of the most important economic activities for economic growth. Hence, by taking various measures to save the environment the banking sector can play a crucial role in promoting environmentally sustainable and socially responsible investment.
As such, Green Banking is also known as 'Ethical Banking'or 'Sustainable Banking'. The purpose of green banking initiatives taken by the central bank is to ascertain required measures to save the environment and reduce pollution while serving or financing the customers and improve in-house environment management through efficient and effective use of resources in all the branch and head offices of the banks.
Any society needs products and services and the businesses rely on infrastructure and governmental service. From the society's perspective, a flow of revenue comes from the businesses, such as income tax from companies, special product taxes, tax deducted from employees' salaries, value added tax and other service charges. On the other hand, the companies generate costs for the society for infrastructure, social welfare and medical care. Without businesses, revenues disappear but most of the costs remain. The interdependence between businesses and the society is complex.
In cost benefit analyses, is it possible to calculate the net value a company generates for the society where it operates?
There must be a balance between society and the companies in a sustainable economy where CMAs can prepare a sustainable business and value creation model for each company.
A CMA can formulate an action plan for the organisation in regards to pollution prevention, product stewardship, and clean technology, which all move a company toward sustainability. A vision of sustainability for an organisation or a company is like a road map to the future value creation, showing the way products and services must evolve and what new competencies will be needed to achieve sustainability.
As requirement of sustainability, an enterprise must consider environment while carrying out its activities and should think about future generations as they meet the needs of today's consumers and they must perform their activities on this perspective.
Considering the production factors in order to meet continuity of business and demands of consumers based on environmental issue, a cost accountant has to define and measure environmental costs of activities to be done during the period and to minimise the potential environmental costs via environmental management accounting. Environmental management accounting requires planning environmental impacts of main and other activities carried out during the period and the management of costs emerge.
A CMA will also establish an independent 'sustainable department' in order to address the risks identified on the basis of sustainable business operation and will prepare a sustainability report based on internationally recognised standard. By preparing sustainability report, it can be ensured that organisations consider their impacts on sustainability issues, and enables them to be transparent about the risks and opportunities they have.
Md. Touhidul Alam Khan is Deputy Managing Director at Prime Bank Ltd. and a fellow member of Institute of Cost & Management Accountants of Bangladesh (ICMAB).