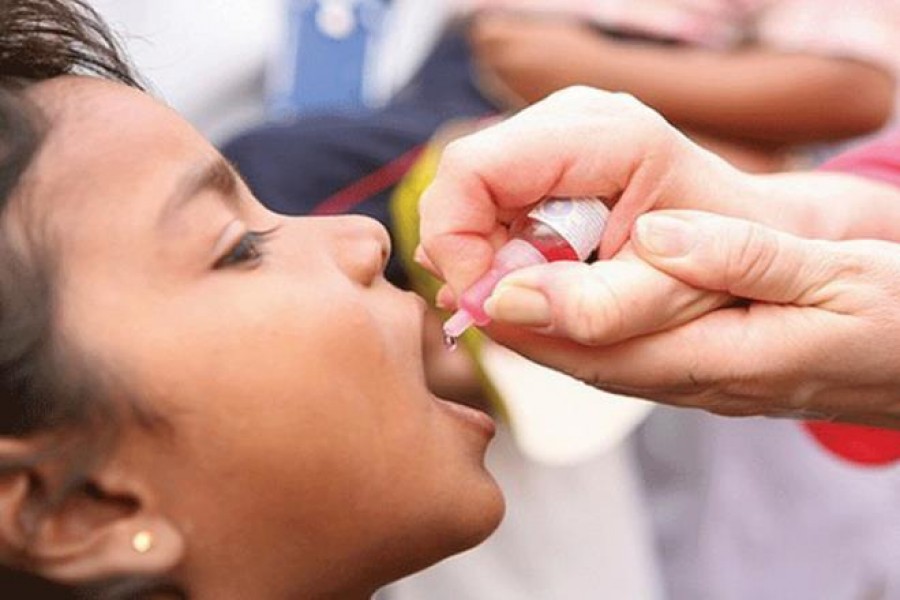
The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF on Wednesday warned of an alarming decline in the number of children receiving life-saving vaccines around the world amid coronavirus pandemic and called for immediate efforts to this end.
The UN organisations said this drop is due to disruptions in the delivery and uptake of immunisation services caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to new data by WHO and UNICEF, these disruptions threaten to reverse hard-won progress to reach more children and adolescents with a wider range of vaccines, which has already been hampered by a decade of stalling coverage.
The latest data on vaccine coverage estimates from WHO and UNICEF for 2019 shows that improvements such as the expansion of the HPV vaccine to 106 countries and greater protection for children against more diseases are in danger of lapsing.
For example, preliminary data for the first four months of 2020 points a substantial drop in the number of children completing three doses of the vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (DTP3).
This is the first time in 28 years that the world could see a reduction in DTP3 coverage – the marker for immunisation coverage within and across countries.
“Vaccines are one of the most powerful tools in the history of public health, and more children are now being immunised than ever before,” said Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO director-general.
“But the pandemic has put those gains at risk. The avoidable suffering and death caused by children missing out on routine immunisations could be far greater than COVID-19 itself. But it doesn’t have to be that way. Vaccines can be delivered safely even during the pandemic, and we are calling on countries to ensure these essential life-saving programmes continue.”
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, at least 30 measles vaccination campaigns were or are at risk of being cancelled, which could result in further outbreaks in 2020 and beyond.
According to a new UNICEF, WHO and Gavi pulse survey, conducted in collaboration with the US Centers for Disease Control, the Sabin Vaccine Institute and Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, three quarters of the 82 countries that responded reported COVID-19 related disruptions in their immunisation programmes as of May 2020.
The reasons for disrupted services vary. Even when services are offered, people are either unable to access them because of reluctance to leave home, transport interruptions, economic hardships, restrictions on movement, or fear of being exposed to people with COVID-19.
Many health workers are also unavailable because of restrictions on travel or redeployment to COVID response duties as well as a lack of protective equipment.
“COVID-19 has made previously routine vaccination a daunting challenge,” said UNICEF executive director Henrietta Fore.
“We must prevent a further deterioration in vaccine coverage and urgently resume vaccination programmes before children’s lives are threatened by other diseases. We cannot trade one health crisis for another.”