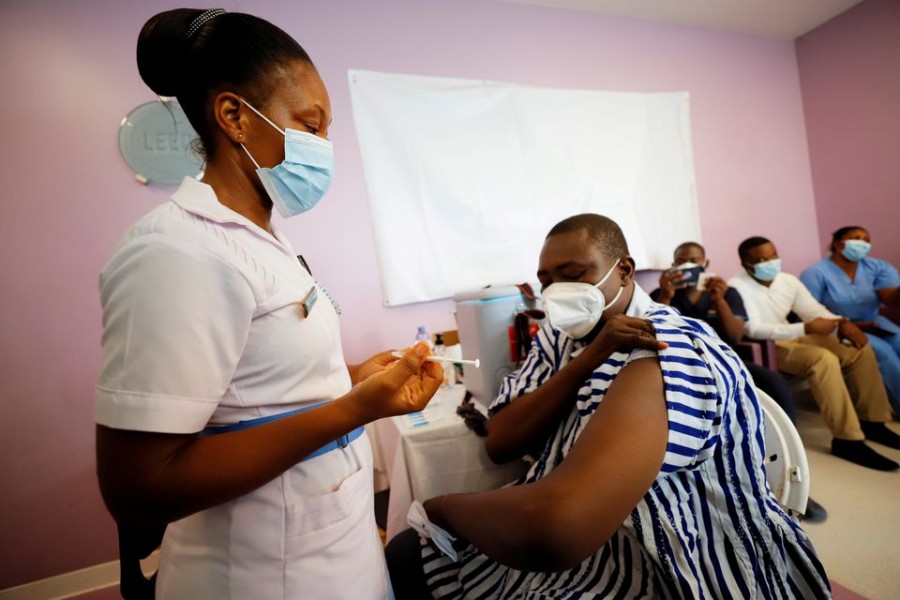
The Covid pandemic will "go on for a year longer than it needs to" because poorer countries are not getting the vaccines they need, the World Health Organization (WHO) says.
Dr Bruce Aylward, senior leader at the WHO, said it meant the Covid crisis could "easily drag on deep into 2022".
Less than 5 per cent of Africa's population have been vaccinated, compared to 40 per cent on most other continents.
The UK has delivered more than 10 million vaccines to countries in need, reports the BBC.
It has pledged a total of 100 million.
Dr Aylward appealed to wealthy countries to give up their places in the queue for vaccines in order that pharmaceutical companies can prioritise the lowest-income countries instead.
He said wealthy countries needed to "stocktake" where they were with their donation commitments made at summits such as the G7 meeting in St Ives this summer.
"I can tell you we're not on track" he said. "We really need to speed it up or you know what? This pandemic is going to go on for a year longer than it needs to."
The People's Vaccine - an alliance of charities - has released new figures suggesting just one in seven of the doses promised by pharmaceutical companies and wealthy countries are actually reaching their destinations in poorer countries.
The vast majority of Covid vaccines have been given in high-income or upper-middle-income countries. Africa accounts for just 2.6 per cent of doses administered globally.
The group of charities, which includes Oxfam and UNAids, also criticised Canada and the UK for procuring vaccines for their own populations via Covax, the UN-backed global programme to distribute vaccines fairly.
Official figures show that earlier this year the UK received 539,370 Pfizer doses while Canada took just under a million AstraZeneca doses.
The original idea behind Covax was that all countries would be able to acquire vaccines from its pool, including wealthy ones. But most G7 countries decided to hold back once they started making their own one-to-one deals with pharmaceutical companies.
Oxfam's Global Health Adviser, Rohit Malpani, acknowledged that Canada and the UK were technically entitled to get vaccines via this route having paid into the Covax mechanism, but he said it was still "morally indefensible" given that they had both obtained millions of doses through their own bilateral agreements.
"They should not have been acquiring these doses from Covax," he said. "It's nothing better than double-dipping and means that poorer countries which are already at the back of the queue, will end up waiting longer."
The UK government pointed out it was one of the countries which had "kick-started" Covax last year with a donation of £548m.
The Canadian government was keen to stress that it had now ceased to use Covax vaccines.
The country's International Development Minister, Karina Gould, said: "As soon as it became clear that the supply we had secured through our bilateral deals would be sufficient for the Canadian population, we pivoted the doses which we had procured from Covax back to Covax, so they could be redistributed to developing countries."
Covax originally aimed to deliver two billion doses of vaccines by the end of this year, but so far it has shipped 371m doses.